Strategic Planning
Driving sustainable growth by defining and implementing effective top-down and bottom-up strategies
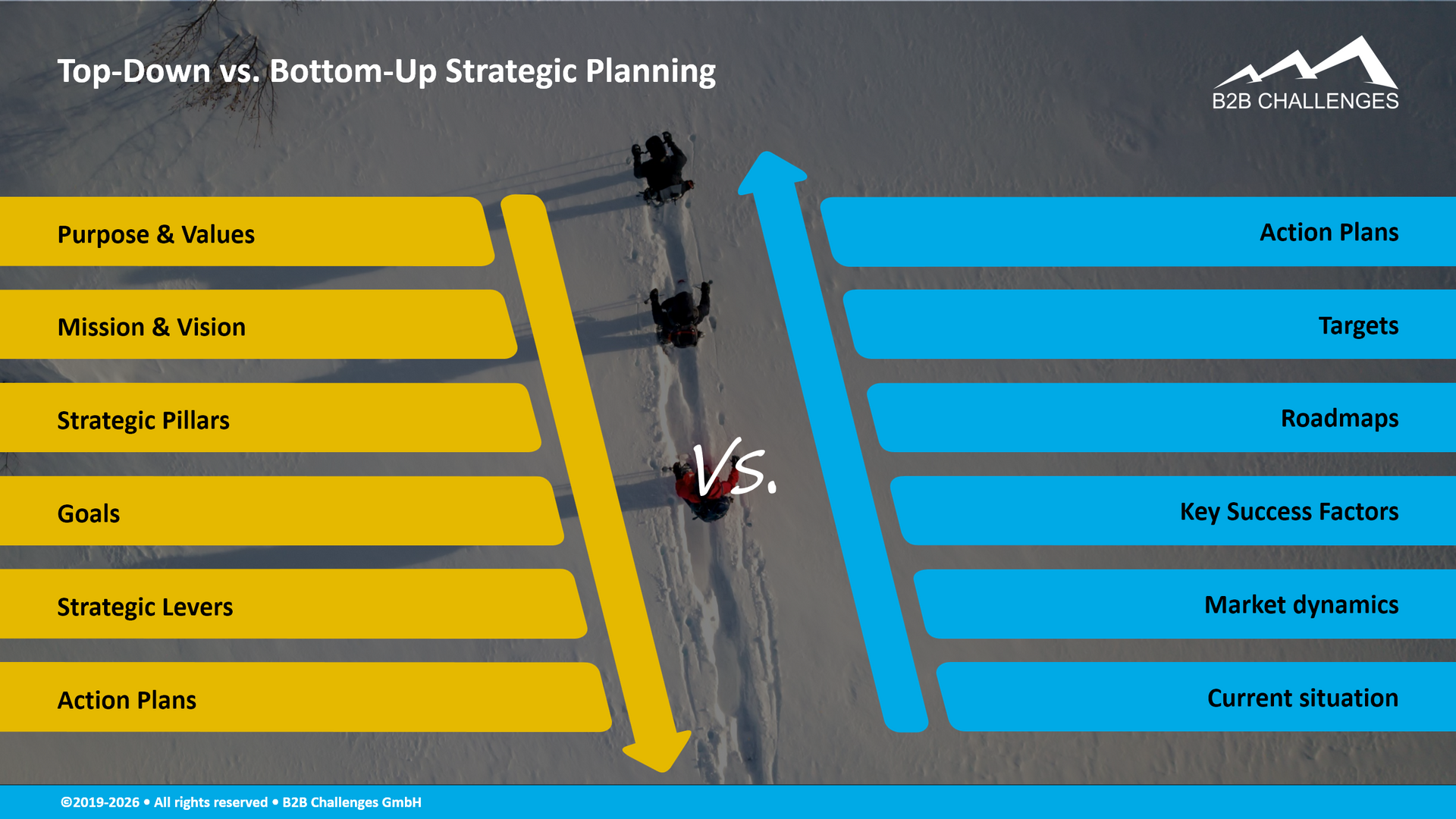
Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Strategic Planning
Strategic planning can be carried out in a top-down or bottom-up manner. They are complementary methods, one more strategic and often more ambitious, the other more pragmatic and often more realistic. It is therefore generally beneficial to carry out both types of strategic planning, sequentially or in parallel. Combining them allows for a more complete analysis of the organization's strategic context, real-time feedback from both employees and customers, better exploitation of collective intelligence and increased team commitment. In short, the combination of the two methods provides a balanced and comprehensive approach to strategic decision-making.
Top-Down Strategic Planning
Top-down strategic planning provides organizations with clear and consistent strategic direction. The process begins with defining the organization's purpose, values, mission, and vision, which together shape its positioning. Building on this foundation, senior management establishes the strategic pillars (the framework for executing the strategy), sets the objectives, and defines the strategic levers (the means and tactics that will enable the objectives to be achieved). These elements are then translated into strategic action plans. Typically driven by the executive committee, this centralized approach ensures that all activities within the organization are aligned with the implementation and achievement of its strategy.
Bottom-Up Strategic Planning
Bottom-up strategic planning starts with an extensive analysis of the current situation, market dynamics and emerging trends. Based on these insights, organizations identify key success factors (the conditions, skills and resources required for success). This fundamental preparation enables roadmaps to be drawn up, objectives to be set and action plans to be defined. Generally carried out on a decentralized basis, often at commercial segment or business unit level, this approach not only ideally complements top-down strategic planning, but also promotes operational efficiency, employee commitment, development and empowerment.
Go-to-Market strategy
A strong go‑to‑market strategy connects business ambition with real market execution. It defines how an offering is positioned, priced, launched, and scaled across regions, channels, and customer segments, while aligning product, marketing, sales, and partners around a shared value proposition. By clarifying who to target, why customers should care, and how buying decisions are influenced, it reduces friction in the customer journey and increases commercial impact. In complex B2B environments, a well-designed go‑to‑market approach enables faster adoption, sustainable growth, and measurable return on investment.
Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic framework that allows B2B organizations to visualize and align the nine essential building blocks of value creation. By mapping the interplay between customer segments, value propositions, and operational structures, businesses can identify critical dependencies and hidden opportunities within their value chain. This holistic approach allows to navigate complex buyer relationships and to optimize resource allocation. It transforms abstract strategy into a clear, actionable roadmap, ensuring that every partnership and activity directly supports sustainable revenue growth and competitive differentiation.
From available market to serviceable and obtainable market
Effective strategic planning starts with understanding not just how big a market is, but how much of it a company can truly reach and win. Moving from broad market potential to realistic opportunity requires progressively narrowing the focus—from theoretical demand to what is addressable, serviceable, and ultimately obtainable. This structured market-sizing logic helps leaders avoid overestimating growth, align ambition with capabilities, and ground investment decisions in reality. It provides a shared language for strategy, sales, and finance, enabling clearer priorities, stronger go‑to‑market choices, and more credible growth plans.
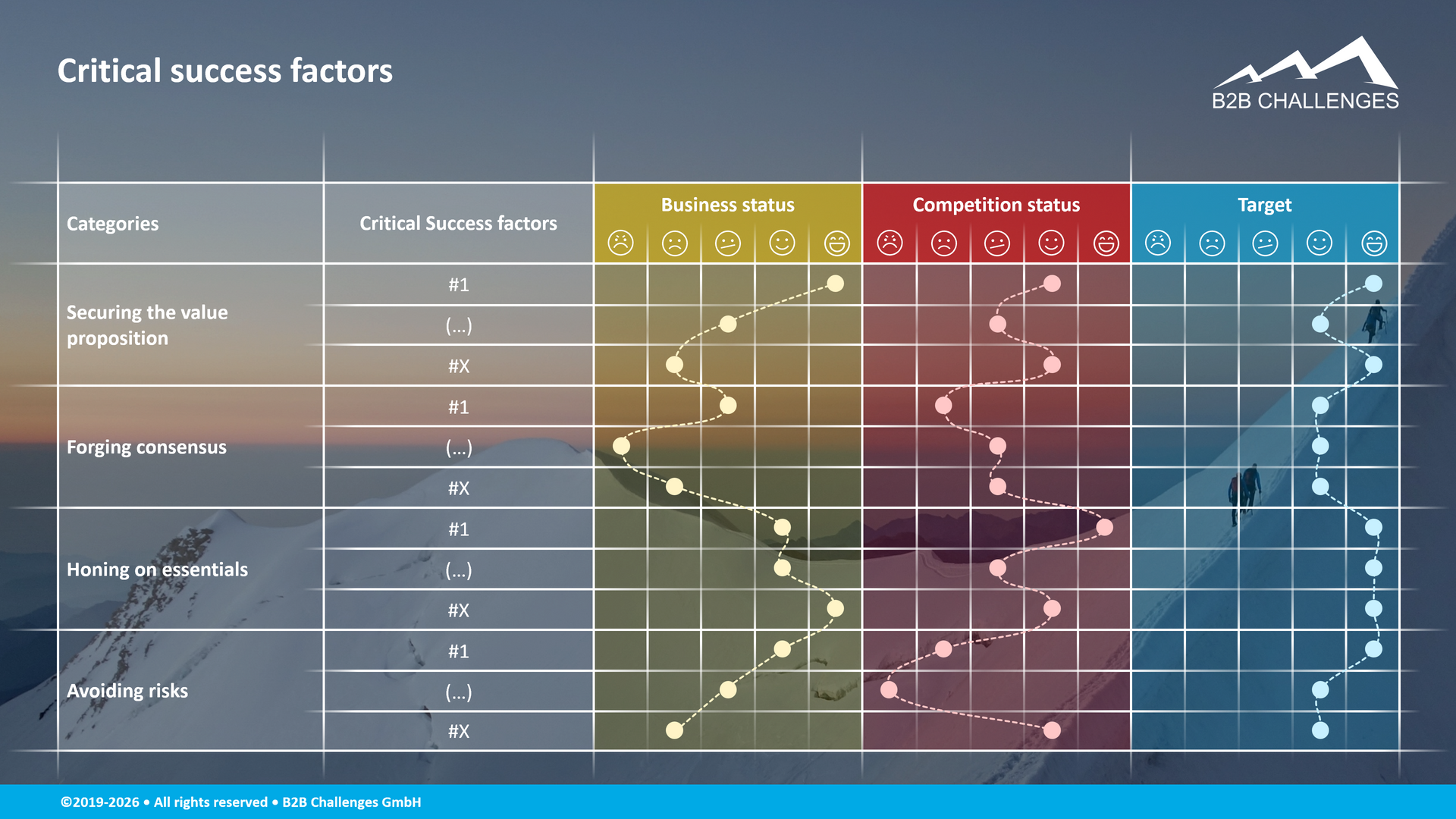
Critical success factors
Sustainable strategy execution depends on a clear understanding of the few factors that truly determine success. Critical success factors translate strategic intent into practical priorities by clarifying what must go right in a given competitive and organizational context. They help leaders secure a compelling value proposition, align stakeholders around shared choices, focus resources on what matters most, and proactively manage risks. By grounding ambition in business realities, competitive dynamics, and target outcomes, critical success factors provide a disciplined foundation for effective strategic planning and decision‑making.
Execution and transformation requirements
Effective strategic planning requires the clear identification of outstanding execution and transformation requirements for critical success factors that have not yet been established. Execution requirements focus on closing immediate gaps in capabilities, resources, and processes to deliver objectives. Transformation requirements address fundamental shifts in organization, culture, and technology that typically require more complex measures and are inherently harder to implement. By addressing both in parallel, organizations ensure the consistent implementation of missing critical success factors while simultaneously building the foundations for long-term strategic resilience.
The content of this page is not exhaustive and will be completed from time to time.